Book – Virtualizing Microsoft Tier 1 Applications with VMware vSphere 4
I got the honor of talking with Charles Windom today. He is the author of “Virtualizing Microsoft Tier 1 Applications with VMware vSphere 4”
We were concerned about Exchange performance with our SAN being setup as a large aggregate of drives vs. discrete drives.
All the best practices I read specifically stated discrete drives for performance reasons with Exchange 2003. However our SAN is setup as a large aggregate of drives.
Sean Dehlinger of vmware set me up with Charles and in about 2 minutes I had the confirmation that I needed.. (Thanks Sean!)
Here is the feed back from Charles…
1. Exchange 2003 Database does lots of Random R/W’s to the LUN, if the LUN is not discrete then you will see delays. The Logs and C: Drive are doing more Sequential R/W’s and the LUN aggregate should be okay.
2. IF your using Exchange 2010 Database or Logs then the R/W’s are Sequential and LUN discreteness is a non-issue.
It was nice to talk to an true expert and I look forward to meeting him at vmworld 2010 or having him talk at our Phoenix event..
ESX – Using USB to IP Adapeters
Here are some IP to USB Adapters that I know have worked with ESX…
Multi VM Use –http://www.lantronix.com/device-networking/external-device-servers/ubox.html
Single VM Use – http://www.digi.com/products/usb/anywhereusb.jsp#overview
I’ve worked with the DIGI models and they have pretty well…
One note – if you are working with a true VM then you need to enable Windows USB features…
Special Steps for VMware ESX Server Virtual Machines
Since ESX Server does not provide direct support for USB, USB drivers are not installed in the
guest operating system by default. The AnywhereUSB device depends on the USB core files to
install properly.
To enable the rest of the installation to proceed normally, copy and rename the required file from the original operating system CD.
• Source: usbd.sy_ in the \I386 directory of the CD
• Destination: usbd.sys in the \system32\drivers directory of the guest operating system
After copying this file, reboot your machine. You can then continue with the normal
AnywhereUSB installation.
VMware vExpert 2010
The other day I was selected as a VMware vExpert for 2010. John Troyer (of VMWARE) is building a great community of vExperts with like minded individuals that are proponents of virtualization evangelism. On another note I nominated my entire Phoenix VMUG Team (Luke, Rob, Duke, and Charles) for the award and they all were excepted ! Congrats Guys, you have earned it.
For those of you that do not know, the VMware vExpert program was created in 2009 to show appreciation for those individuals who have significantly contributed to the community of VMware users over the past year. For more information on the program visit the vExpert site
HP c7000 Mid-Plane Replacement
If you’re reading this blog, I’m hoping you never have to do this procedure. However the other day we had a c7000 Mid-plane go out.
We first noticed some odd issues with Ethernet NICs randomly disconnecting. Then, our chassis started to fail entire Ethernet pass through modules, it came back online and then a few weeks later just one Ethernet port stayed in a failed state. Working with HP and our local VAR we tried all the troubleshooting steps and found it was the mid-plane had failed.
This blog post is merely my notes and some of my findings during the replacement of the mid-plane. I worked with an HP certified technician and he had a punch list from HP to complete this repair. I recommend a certified technician do the repair as you never know what you’re going to run into and we did run into a few gotchas that stumped us all.
Quick Disclaimer – This is not a guide for repairing this device but merely my notes…
First thing – The Plan:
- 7:00 Migrate VM’s to BC2 (BC = blade chassis) and shut down ESX hosts on BC1
- 8:00 Shutdown remaining blades in BC1
- 8:20 Start Repair on BC1
- 8:40 Test repair on BC1
- 8:50 bring up Blades on BC1
- 9:00 TEST applications
- 9:10 Migrate VM’s from BC2 to BC1
- 10:00 Finish
The Plan with Notes:
7:00 Migrate VM’s to BC2 (BC = blade chassis) and shut down ESX hosts in BC1
- No issues, vMotion worked without issues & shutdown 6 ESX hosts via vCenter Server
8:00 Shutdown remaining blades in BC1
- No issues, shut down blade servers
8:20 Start Repair on BC1
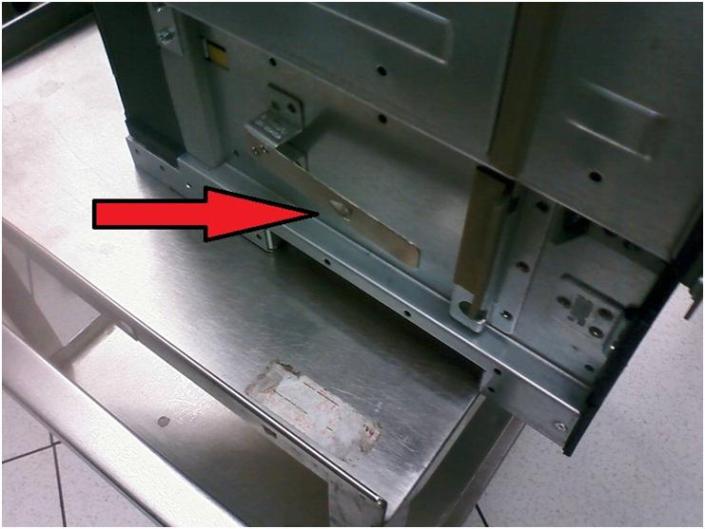
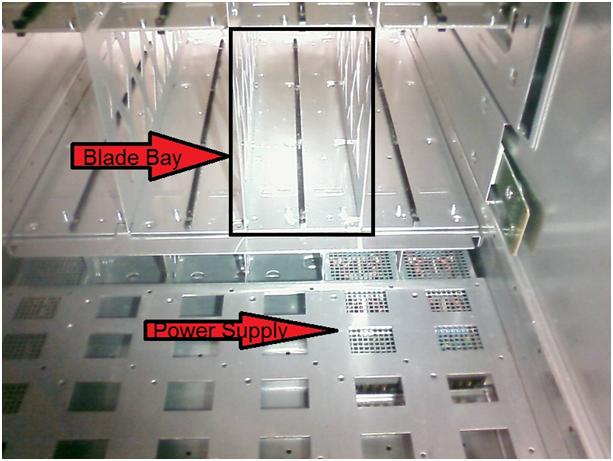
Power down the c7000 chassis, remove all the cards, power supplies and blades
This is a pic where we removed the rear cards. One thing we were able to do was remove the Ethernet & Fibre Pass through cards without having to disconnect the cables.
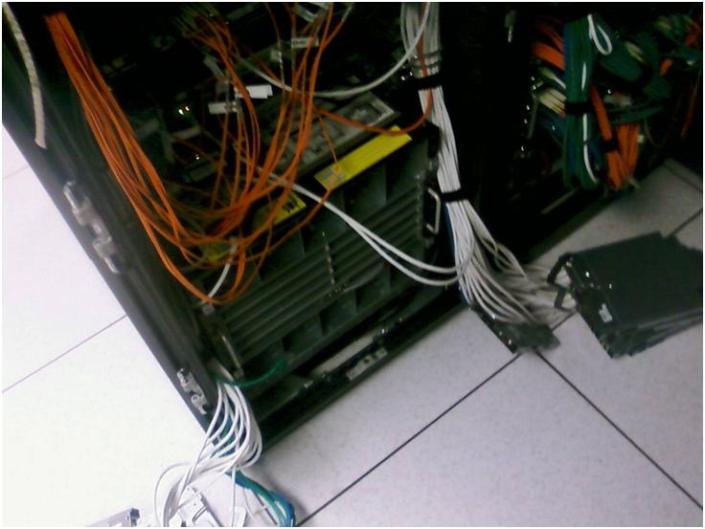

Second shot of the removal
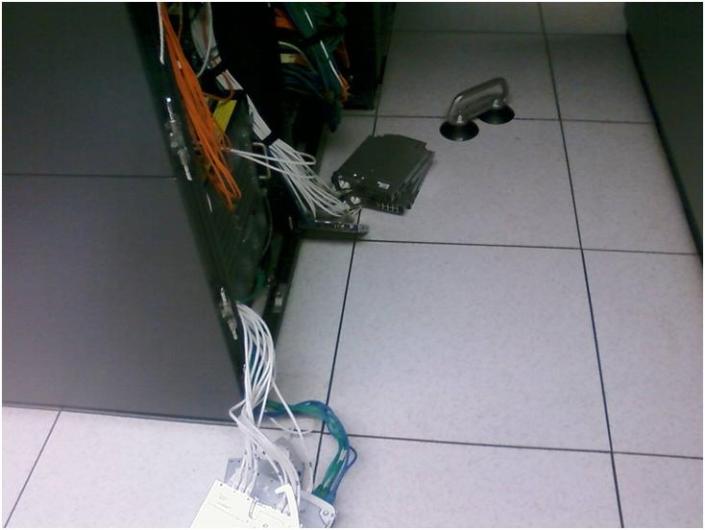

Remove the blades and Power supplies
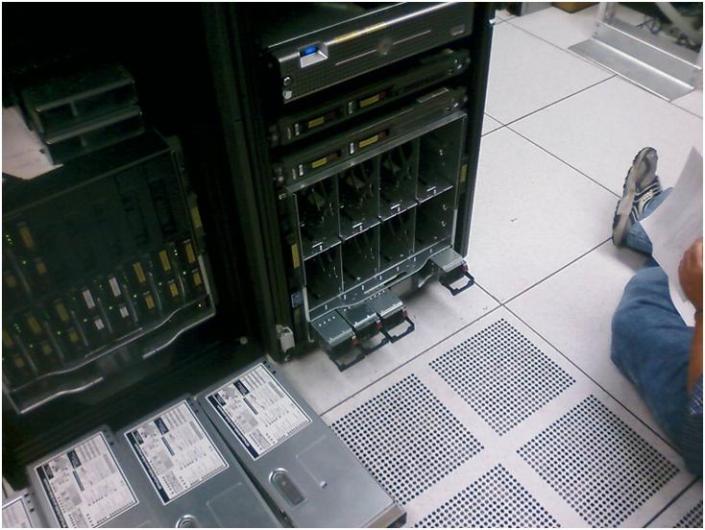

To remove the mid-plane there were four bolts holding in it in place. We removed them and then pull it till it stops. The retaining clips needed depressed to allow the unit to be removed and we pressed them in and it removed with ease. Note: The manual fails to mention this.
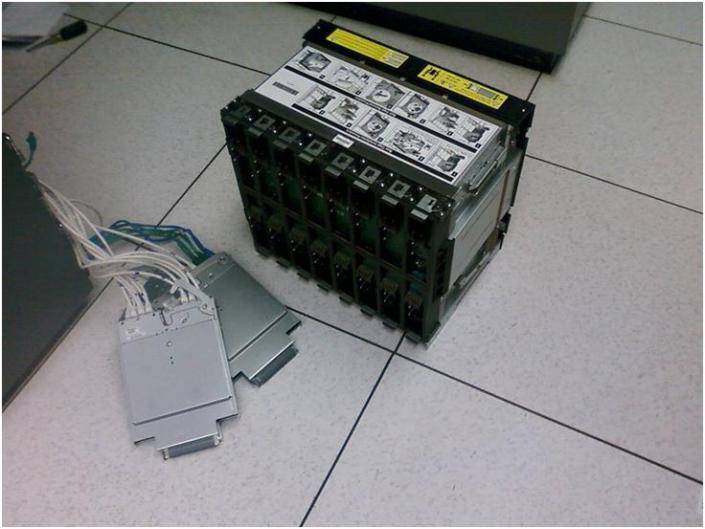

Here is a shot of the retaining clips. They help to hold the mid-plane in. At first we could not figure out why the mid-place would not come out. This held us up a bit as the instructions failed to mention depressing them to allow the mid-plane removal.

Inside the blade chassis – Rear
After removing the mid-plane chassis there are several bolts that hold in this together. One item you have to do is remove the foam tape in the screen shot below.
This will allow you to separate the mid-plane board from the chassis. This was another gotcha that the instructions failed to mention this step.
Our package came with replacement tape, yours may vary.
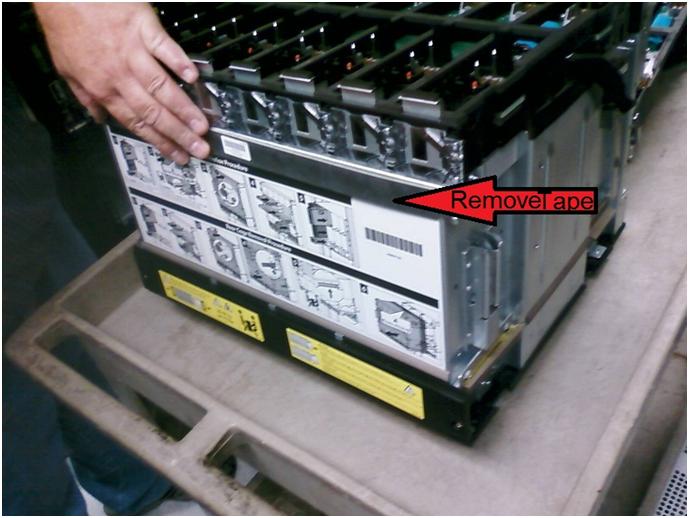

After replacing the mid-plane board we reassemble the chassis in this order..
- Reinserted the Mid-Plane chassis
- ilo Control Modules
- Power Supplies
- Powered on device, wait
- Inserted pass though modules, wait
- Inserted Blades and powered them on
9:00 Ensure the Blades on BC1 are reporting in
-
No issues, everything is now working!
9:15 TEST applications
-
No issues, all blades and apps came right up
9:30 Migrate VM’s from BC2 to BC1
- No Issues, all VM’s migrated perfectly
10:00 Finish
Gotchas / Notes
2 Items slowed us down
- The retaining clips on the lower right and left hand sides were not noted in the documentation. We had lots of cables on the left and right side so it made it hard to clearly see where they were.
- The tape holding on the mid-plane board wasn’t documented. It took us a bit to figure out that a simple piece of foam tape could hold together, but it did.
Next time I mount a c7000 chassis I’ll remember to mount it about 4U from the base of a rack. The issue we were having was the cabling and PDU power cords were getting in the way of the mid-plane and this made it harder to remove.
Other than these minor issues, the repair went smooth, and it was fun to see the “guts” of a c7000.
Home Lab – Workstation 7 to 7.1 Upgrade
I upgraded my Home Lab from Workstation 7.0 to 7.1 tonight..
More info on my home lab here…
http://vmexplorer.blogspot.com/2010/02/home-lab-install-of-esx-35-and-40-on.html
Upgrade Steps I took…
- First step was to uninstall Workstation 7, then install 7.1
- Note: The install will do this automatically if needed
- Once the uninstall is completed a reboot is necessary
- After the reboot I noticed Windows 7 reconfigure the Network adapters
- Note.. At this point if you need to adjust your local subnets now might be a good time, once you install 7.1 it will reconfigure all the vmnets around this.
- The install of Workstation 7.1 is pretty simple, Choose Custom and Next a few times and one reboot
- After the reboot Windows 7 finds the new network adapters, and it was all done..
What I noticed after the upgrade..
- WS7.1 launched with out issues, it didn’t require me to input my serial number again, and it came right up.
- I opened up the Virtual Network Editor, and it took about a minute to assign subnets to the 8 difference vmnets. (This is something I should have documented better, as I don’t recall all the subnets. However I did have 2 documented)
- When I powered on my good old XP VM, locally Windows 7 noticed this as needing an USB updated driver, it quickly went to the update site and downloaded the driver, no issue. In the XP VM I updated the vmware tools, rebooted, and it worked normally
- One new thing was the vmtools ICON now is grey and white
- I powered up my ESX test environment..
- 1st my vCenter Server is connected to VMnet0 in Auto-Bridged mode
- On Power up I noticed my vm had been switched from a static ip to DHCP
- I correct this by entereing its static IP and it functioned normally
- 2nd I powered up my ESX 3.5 host
- It booted fine and attached itself to the vCenter server without issue
- 3rd I powered up my ESX 4.0 host
- It booted fine and attached itself to the vCenter server without issue
Final thoughts…
This upgrade was a good warm up for the next Workstation upgrade that I need to do.
This environment was pretty simple, nothing very complex, and pretty much went smoothly.
I think the best rule of thumb is before you upgrade know and document your lab then upgrade.
My home lab was partially documented it would have went smoother if it was fully documented.
Next up… Update of a more complex WS lab with an IOMega iSCSI NAS and multiple subnets…
I’ll post up how it goes…
Here’s whats new with WS7.1… I got this from VMware site…
http://www.vmware.com/support/ws71/doc/releasenotes_ws71.html#whatsnew
What’s New
This release of VMware Workstation adds the following new features and support:
•New Support for 32-Bit and 64-Bit Operating Systems
•New Features in VMware Workstation
New Support for 32-Bit and 64-Bit Operating Systems
This release provides support for the following host and guest operating systems:
Operating System Host and Guest Support
Ubuntu 8.04.4 Host and guest
Ubuntu 10.04 Host and guest
OpenSUSE 11.2 Host and guest
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.5 Host and guest
Fedora 12 Guest
Debian 5.0.4 Guest
Mandriva 2009.1 Guest
New Features in VMware Workstation
•OpenGL 2.1 Support for Windows 7 and Windows Vista Guests — Improves the ability to run graphics-based applications in virtual machines.
•Improved Graphics Performance — Enhanced performance with better benchmarks, frame rates, and improved rendering on Windows 7 and Windows Vista guests allows you to run various graphics-based applications. In addition, major improvements in video playback enable you to play high-resolution videos in virtual machines.
•Automatic Software Updates — Download and install VMware Tools and receive maintenance updates when available.
•Direct Launch — Drag guest applications from the Unity start menu directly onto the host desktop. Double-click the shortcut to open the guest application. The shortcut remains on the desktop after you exit Unity and close VMware Workstation.
•Autologon — Save your login credentials and bypass the login dialog box when you power on a Windows guest. Use this feature if you restart the guest frequently and want to avoid entering your login credentials. You can enable Autologon and use direct launch to open guest applications from the host.
•OVF 1.1 Support — Import or export virtual machines and vApps to upload them to VMware vSphere or VMware vCloud. The VMware OVF Tool is a command-line utility bundled in the VMware Workstation installer. Use this tool along with VMware Workstation to convert VMware .vmx files to .ovf format or vice versa. VMware recommends that you use the OVF command-line utility. For more information, see the OVF Web site and OVF Tool User Guide.
•Eight-Way SMP Support — Create and run virtual machines with a total of up to eight-processor cores.
•2TB Virtual Disk Support — Maximum virtual disks and raw disks size increased from 950GB to 2TB.
•Encryption Enhancements — VMware Workstation includes support for Intel’s Advanced Encryption Standard instruction set (AES-NI) to improve performance while encrypting and decrypting virtual machines and faster run-time access to encrypted virtual machines on new processors.
•Memory Management — User interface enhancements have simplified the handling of increased virtual memory capacity.
•User Experience Improvement Program — Help VMware improve future versions of the product by participating in the User Experience Improvement Program. Participation in the program is voluntary and you can opt out at any time. When you participate in the User Experience Improvement Program, your computer sends anonymous information to VMware, which may include product configuration; usage and performance data, virtual machine configuration; usage and performance data, and information about your host system specifications and configuration.
The User Experience Improvement Program does not collect any personal data, such as your name, address, telephone number, or email address that can be used to identify or contact you. No user identifiable data such as the product license key or MAC address are sent to VMware. VMware does not store your IP address with the data that is collected.
For more information about the User Experience Improvement Program, click the Learn More link during installation or from the VMware Workstation Preferences menu.
vSphere Hot Memory Add
I was playing around with vSphere Hot memory add with ESX 4 U1 on a Windows 2008 ETP x64 VM.
I was simple to configure and could be a quick upgrade…
- In vCenter Server Shutdown the VM
- Right Click > Edit Settings > Options > Under Advanced Choose Memory/CPU Hotplug
-
Enable Memory Hot Add and CPU Hot Plug
- Power on your VM, Go to the Consol for this VM, Wait for it to boot, logon
- I noticed mine had a pop up that it added a snap-in
-
In vCenter Server Right click on the VM, Edit Settings, click on Memory and add the memory you wish..
(Notice you can’t go down only up… You’ll need to power down to do this)
Notes…
I noticed after clicking OK, my vm console screen went blank for about 10 seconds and then it came back.
When it did I had the upgraded memory and all was well.
Here’s a great post with more information…
http://www.boche.net/blog/index.php/2009/05/10/vsphere-memory-hot-add-cpu-hot-plug/
Installing vCenter Server 4 with Windows 2008 64Bit and SQL2008 64Bit
You might be asking yourself what are the benefits of deploying Windows & SQL 2008×64?
So far I have found one… If you want to position your server for x64 and 2008 then this makes sense.
See these articles for more information..
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/149605
Here are the basic steps to setup vCenter 4 with Windows/SQL 2008 x64
This guide is for reference, like all articles I post up, they are my notes, so use them at your own risk…
SQL2008 Install…
- Setup your VM with ample – CPU, RAM, Disk C: for OS and D: SQL Data
- In this case drives are 1 x vCPU, 4GB RAM, C: [50GB] D:[150GB]
- Install Windows 2008 x64 Standard Setup
- Run the setup from the SQL2008 CDROM
- Click on Installation > New SQL Servers
- Click okay if your “SQL Support Rules” succeed
- Click Install to setup the support install files
- Validate that all Setup Support Rules status are Passed (if not remediate), click next
- Click next to Product Key
- Click next to accept the terms
- Choose Database Engine Services, All Management Tools – Basic, Click Next
- Change the location of the “Instance Root Directory” to your D: drive using the default folder path, Click Next
- Confirm Disk Usage Summary, Click Next
- Choose “NT Authority\SYSTEM” for the account for SQL Agent & Database Engine, Click Next
- Choose Mixed Mode, Enter the “sa” password, Click on Add Current User Or Add your own, Click Next
- Click Next to validate install Rules
- Remediate issues if necessary, else Click Next
- Click install to start installation, Allow to complete the install of SQL 2008
- Click Next to complete and close to exit
- Validate your install by opening SQL Server Management Studio
- Ensure the SQL Server Agent Service is set to Automatic and is started
SQL2008 Prep for vCenter Server
- Open SQL Server Configuration Manager, Click on SQL Server Network Configuration, Choose Protocols for MSSQLserver, Right click on named pipes and choose enable, Restart the SQL Services or reboot
- Apply any vmware approved SQL Patches (Ensure a snapshot, backup or other has been taken)
- Create the user vcdb, Click on security > Logins > Right Click Choose New User
- Type in the user vcdb
- Choose SQL Server Authentication then enter a password
- Uncheck Enforce Password Expiration
- On the left, click on Server Roles
- Choose sysadmin, then click on OK
- Create the Database vcdb, Right Click on Databases > choose New Database
- Enter the Name vcdb for the database name
- Click on ‘….’ to add the owner, use vcdb as the owner, click OK
- On the left, click on Options, choose simple for recovery mode
- Choose OK at the bottom
- Click on Security > logins > right click on vcdb choose properties
- Change default database to vcdb, choose OK
- Create the user vmupd, Click on security > Logins > Right Click Choose New User user
- Type in vmupd
- Choose SQL Server Authentication then enter a password
- Uncheck Enforce Password Expiration
- On the left, click on Server Roles
- Choose sysadmin, then click on OK
- Create the database vmupd, Right Click on Databases > choose New Database
- Enter the Name vmupd for the database name
- Click on ‘….’ to add the owner, use vmupd as the owner, click ok
- On the left click on Options, choose simple for recovery mode
- Choose OK at the bottom
- Click on Security > logins > right click on vmupd choose properties
- Change default database to vmupd, choose OK
Setup ODBC Connectors…
- Create a link to the 32Bit ODBC Admin tool (C:\Windows\SysWOW64\odbcad32.exe)
- Open the 32Bit ODBC Data Source Admin
- Create System DSN for vcdb database, Click on System DSN Tab
- Click on Add
- Choose ‘SQL Native Client 10.0’ (Don’t Choose SQL Native Client only)
- Enter the database name of vcdb
- For Server Choose the local server name, Click on next
- Choose With SQL Server Authentication
- Ensure Connect to SQL is checked
- Enter Login ID of vcdb and the password Click on Next
- Ensure that Change the Default Database to is checked and vcdb appears below it, Click on Next
- Choose Finish
- Click on Test data source and look for TESTS COMPLETE SUCCESSFULLY!
- Click on OK, then OK again
- Create System DSN for vmupd database, Click on System DSN Tab
- Click on Add
- Choose ‘SQL Native Client 10.0’ (Don’t Choose SQL Native Client only)
- Enter the database name of vmupd
- For Server Choose the local server name
- Click on next
- Choose With SQL Server Authentication
- Ensure Connected to SQL is checked
- Enter Login ID of vmupd and the password Click on Next
- Ensure that Change the Default Database to is checked and vmupd appears below it, Click on Next
- Choose Finish
- Click on Test data source and look for TESTS COMPLETE SUCCESSFULLY!
-
Click on OK, then OK again
Install vCenter Server 4
- Open the vCenter Installer
- Choose vCenter Server from the Installer screen
- Choose Ok for English
- If prompted Choose Yes to continue to possible IIS port issues
- Click Next on the Welcome Screen
- Choose I agree to the terms, click next
- Enter your User and Organization Names, Enter your license Key, Click Next
- Choose Use an existing supported database
- Choose the DSN name of vcdb, click next
- Enter the password for vcdb, click next
- Ensure Use System Account is checked, click next
- Click Next for the Default folder name
- Choose create a standalone VMware vCenter Server Instance
- Ensure all the TCP Ports are okay, Adjust as needed (MS KB149605), Click next
- Click on Install
Install vCenter Update Manager
- Open the vCenter Installer
- Choose vCenter Update Manager from the Installer screen
- Choose OK for English
- Click Next on the Welcome Screen
- Choose I agree to the terms, click next
- Enter the user name and password for the vCenter Server system.
- Choose Use and existing support database, Choose vmupd for the DSN, click next
- Enter the password for vmupd, click next
- Leave defaults for Update Manger Ports, If needed choose Yes to Proxy Settings, else Click next
- Click next for default Directories (Ensure more the 20GB for Location for Downloading Patches)
- Click Install to complete
Install vCenter Converter
- Open the vCenter Installer
- Choose vCenter Converter from the Installer screen
- Choose OK for English
- Click Next on the Welcome Screen
- Choose I agree to the terms, click next
- Choose Typical, click next
- Enter username and password for vCenter Server connection, click next
- Click next for default ports
- Click next for default server ID
- Click Install
Install the vCenter Client
- Open the vCenter Installer
- Choose vCenter Client from the Installer screen
- Choose OK for English
- Click Next on the Welcome Screen
- Choose I agree to the terms, click next
- Enter your User and Organization Names, Enter your license Key, Click Next
- Click next on the Custom Setup windows, Choose install vsphere update utility if needed
- Click next for the default install folders
- Click install to finish
Well that’s it… I’m so glad I decided not to post up screen shots!
From here you should be able to bring up vCenter Server via the client, and with some minor configuration pull down updates too..
Good luck…
Introduction to vSphere 4 Link
This link is well worth bookmarking and has been a great reference for me…
http://pubs.vmware.com/vsp40/wwhelp/wwhimpl/js/html/wwhelp.htm#href=welcome/welcome.html
Installing ESX 4.0 and vCenter 4.0 best practices
This is one of my favorite references… I seem to need it from time to time…
Installing ESX 4.0 and vCenter 4.0 best practices
Purpose
This article provides quick reference to the information needed for a trouble free installation of vSphere ESX 4.0 and vCenter Server 4.0.
Note: Because each environment is different, many installation decisions require knowledge and understanding beyond the scope of this article, consult the vSphere 4.0 document set for more detailed information regarding your installation at http://www.vmware.com/support/pubs/vs_pubs.html.
Resolution
Note: Read the VMware vSphere 4.0 Release Notes for known installation issues.
On the vCenter Server
1.Make sure your hardware and operating system requirements are compliant:
Note: For more information, see ESX and vCenter Server Installation Guide and VMware Infrastructure Compatibility Guide.
•Processor – 2 CPUs 2.0GHz or higher Intel or AMD x86 processors. Processor may be higher if the database runs on the same machine.
•Memory – 3GB RAM. RAM requirements may be higher if your database runs on the same machine.
•Disk storage – 2GB. Disk requirements may be higher if your database runs on the same machine.
•Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Express disk requirements. The bundled database requires up to 2GB free disk space to decompress the installation archive.
•Networking – 1Gbit recommended.
2.Make sure your database requirements and patch levels are compliant:
Note: For more information, see VMware Infrastructure Compatibility Guide and vCenter Server Database Patch and Configuration Requirements.
•Microsoft SQL server Database Support:
•Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Express
Note: Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Express is intended to be used for small deployments of up to 5 hosts and/or 50 virtual machines.
•Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Standard edition (SP1, SP2, SP3)
•Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Standard edition (SP2, SP3) 64bit
•Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Enterprise edition (SP1, SP2, SP3)
•Microsoft SQL Server 2005 Enterprise edition (SP2, SP3) 64bit
•Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Standard Edition
•Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Standard Edition 64bit
•Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Enterprise Edition
•Microsoft SQL Server 2008 Enterprise Edition 64bit
•Oracle Database Support:
•Oracle 10g Standard edition (Release 1 [10.1.0.3.0])
•Oracle 10g Enterprise edition (Release 1 [10.1.0.3.0])
•Oracle 10g Standard edition (Release 2 [10.2.0.1.0])
•Oracle 10g Enterprise edition (Release 2 [10.2.0.1.0])
•Oracle 10g Enterprise edition (Release 2 [10.2.0.1.0]) 64bit
•Oracle 11g Standard edition
•Oracle 11g Enterprise edition
3.Download and fill out the vCenter Server Installation Worksheet.
Note: For more information about the fields in this form, see the Required Data for Installing vCenter Server section of the ESX and vCenter Server Installation Guide.
4.The vCenter Server install wizard gives you the option to use the Windows system account or a user-specified account for the purpose of running vCenter Server.
The primary reason to use a user-specified account is to enable the use of Windows authentication for SQL Server.
If you choose this option:
•The user-specified account must be an Administrator on the local machine and act as part of the operating system and login as a service rights.
•You must specify the account name as DomainName\Username in the vCenter Server install wizard.
•You must configure the SQL Server database to allow the domain account access to SQL Server.
5.Make sure your system has all the software prerequisites for vCenter Server:
Note: For more information, see the vCenter Server Prerequisites section of the ESX and vCenter Server Installation Guide.
•Make sure your operating system meets the requirements:
Note: For more information, see the Operating System Compatibility for vSphere Client, vCenter Server, and VMware vCenter Update Manager section of the VMware Infrastructure Compatibility Guide.
•Windows XP Pro SP2 (SP2 required)
•Windows Server 2003, SP1 and SP2 32bit and 64bit all editions
•Windows Server 2003, R2 and SP2 32bit and 64bit all editions
•Windows Server 2008 32bit all editions
•Windows Server 2008 64bit Standard and Enterprise editions
•Make sure that the system you use for your vCenter Server installation belongs to a domain, rather than a workgroup.
•It is critical that you have reliable DNS and Time services.
•During the installation, the connection between the machine and the domain controller must be working.
•Log into the system using an account with local administrator rights. If joining another vCenter Server in Linked Mode, the account must be a local Administrator on both systems.
•The computer name cannot be more than 15 characters.
•Assign a static IP address and host name to the Windows server that will host the vCenter Server system. This IP address must have a valid (internal) DNS registration that resolves properly from all managed ESX hosts.
6.Configure your database prior to the vCenter install, unless you are using default Microsoft 2005 Express:
Note: Schema creation scripts mentioned in the documentation for both Microsoft SQL and Oracle are optional and intended for experienced Database Administrators. The vCenter Server installer performs the schema creation automatically if one does not already exist.
•Microsoft SQL Database:
•As the Database Administrator, use a script to create a local or remote Microsoft SQL Server Database.
Optionally, the database can be created as it was in vCenter 2.5 by using SQL Server Management Studio.
•Configure a SQL Server ODBC Connection
When you install the vCenter Server system, you can establish a connection with a SQL Server database.
•Configure Microsoft SQL Server TCP/IP for JDBC
If the Microsoft SQL Server database has TCP/IP disabled and the dynamic ports are not set, the JDBC connection remains closed. This causes the vCenter Server statistics to malfunction.
•Oracle Database:
•As the Database Administrator, use a script to create a local or remote Oracle database.
•Configure an Oracle Database User
If you plan to use an Oracle database when you install vCenter Server, you must configure the database user.
•Configure an Oracle Connection for Local Access or Configure an Oracle Connection for Remote Access depending on where the database is located.
•Connect to an Oracle Database Locally
7.VMware recommends using a separate database for vCenter Server and vCenter Update Manager.
8.Run the vCenter Server installer using the vCenter Server Installation Worksheet filled out in step 3.
On the ESX Server
1.Make sure your hardware is compliant on the Hardware Compatibility Guide.
This includes:
•System compatibility
•I/O compatibility (Network and HBA cards)
•Storage compatibility
•Backup software compatibility
2.VMware ESX 4.0 only installs and runs on servers with 64bit x86 CPUs. 32bit systems are no longer supported.
3.Make sure Intel VT is enabled in the host’s BIOS.
4.If you are installing to the local disks and SAN is connected to the ESX host, detach the fiber before continuing with the installation.
Note: Do not disable HBA cards in the BIOS.
5.The /, swap, and all the optional partitions are stored on a virtual disk called esxconsole-.vmdk. Set a size minimum of 8GB for this virtual disk.
Note: For /var/log, VMware recommends a separate partition to prevent unexpected disk space constraints due to extensive logging.
